Tables
Technical description - tables
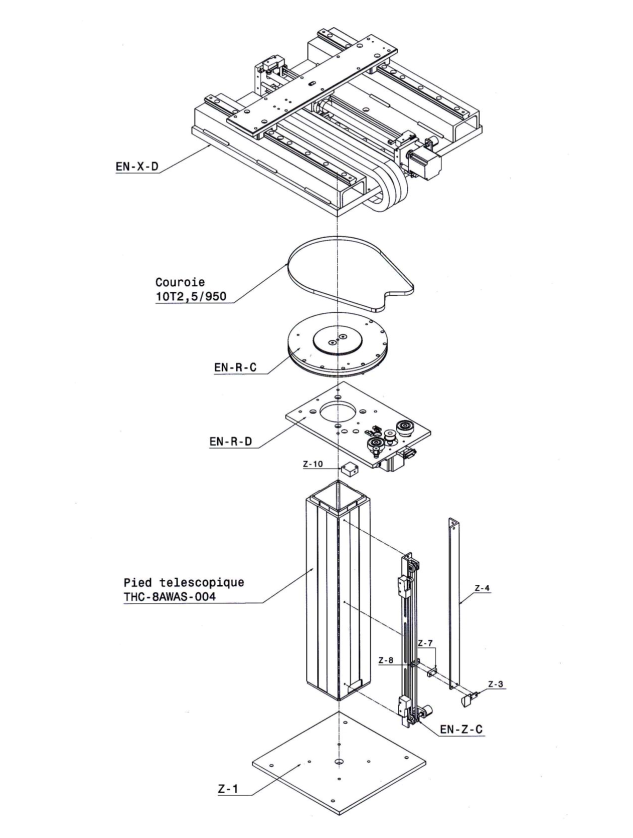
The tables are remote-controlled stages providing the possibility to position the DUT with ±0.1mm precision in the transversal plane (X-Y) with respect to the beam axis. The tables also rotate over the azimuthal angle (θ) in order to achieve a precise alignment with the beam within ±0.025º. The installation of the samples on the table requires the access to the proton area.
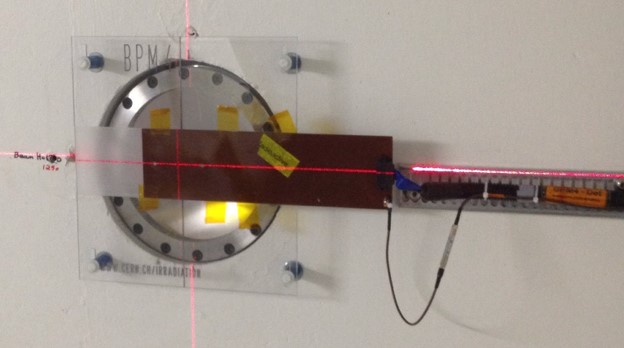
The beam alignemnt with respect to the tables is guaranteed by the beam profile monitor (BPM) in the system.
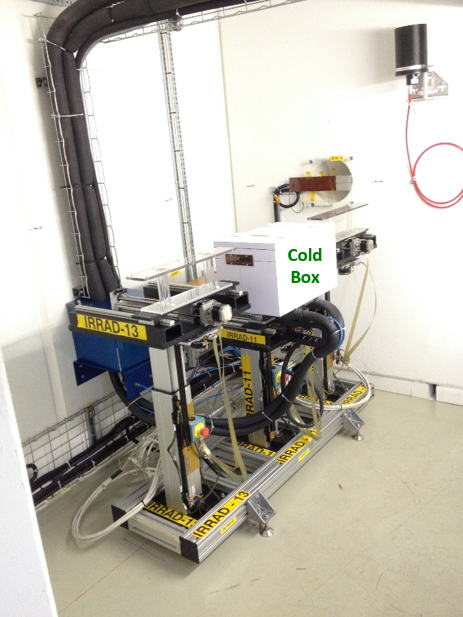
Tables as installed in IRRAD Zone 2

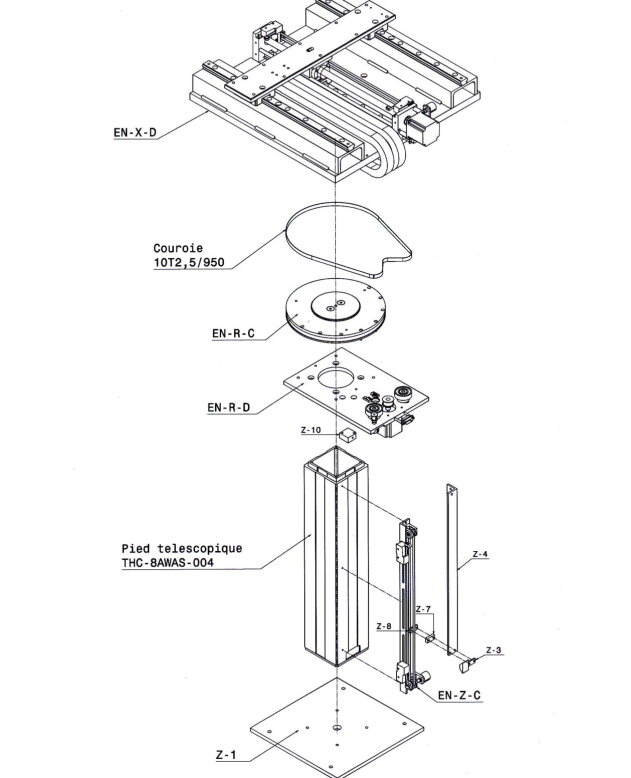
Drawing of the table with its components
BPM in IRRAD
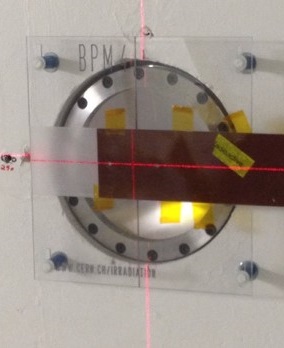
Full description: BPM:
Technical description - cold boxes
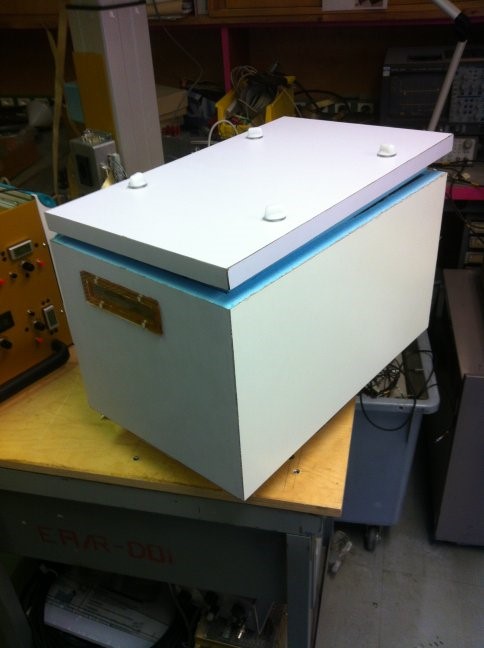
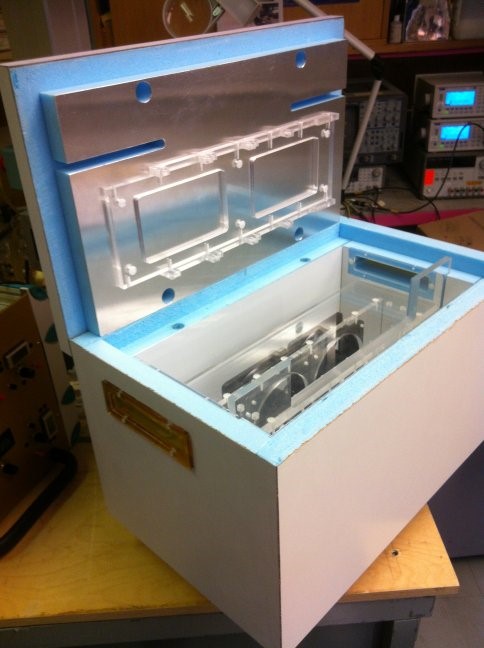
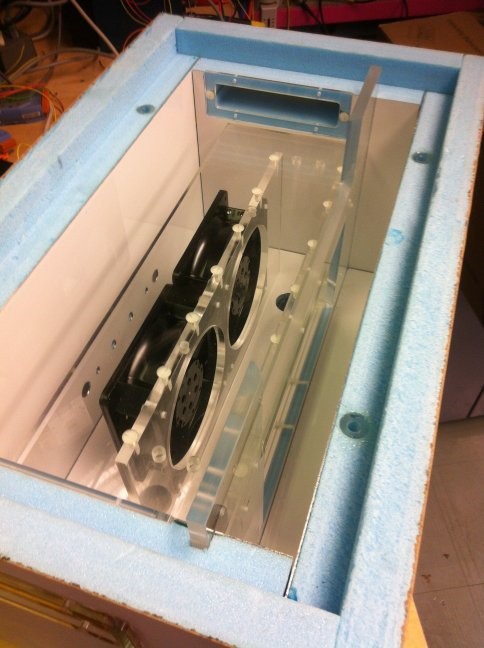
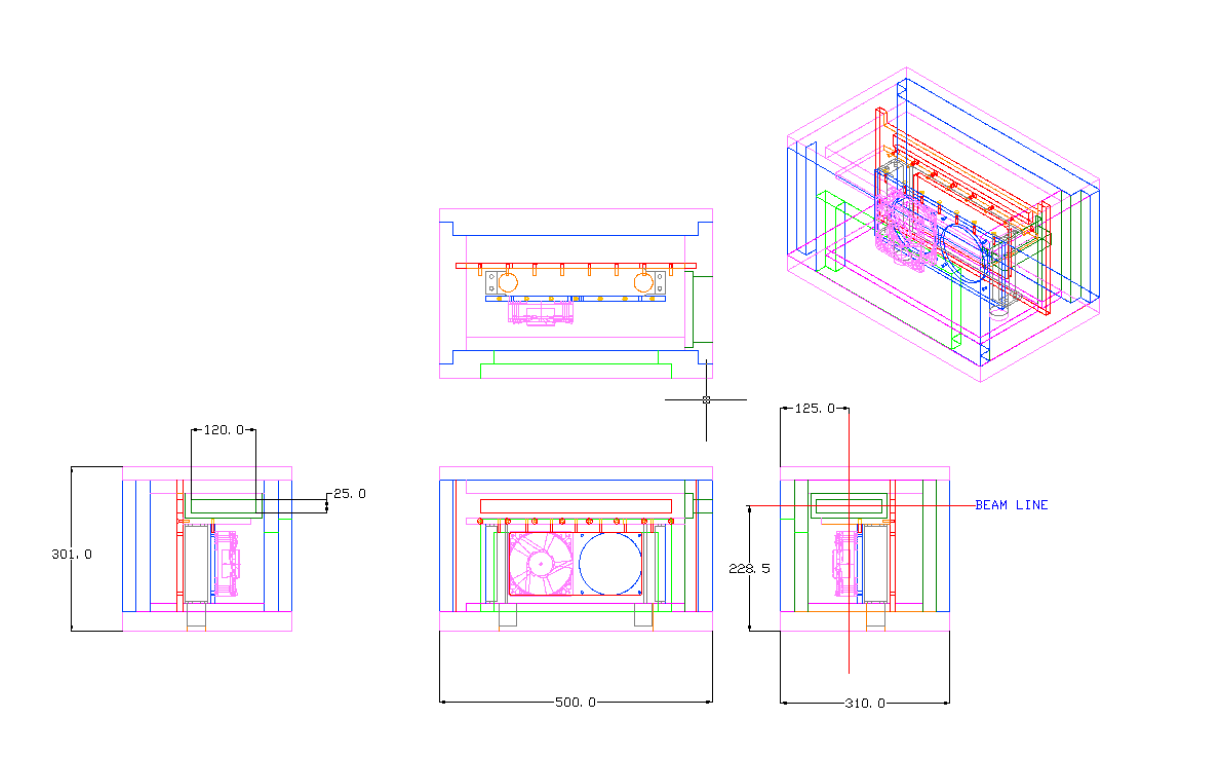
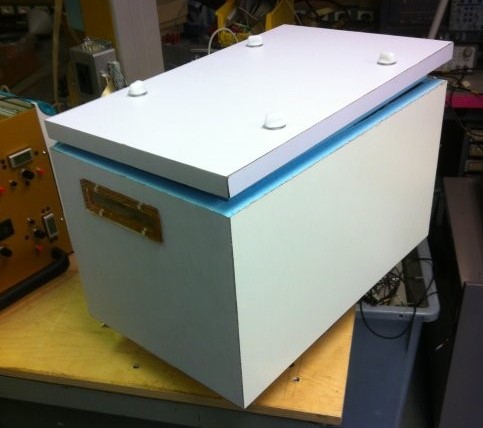
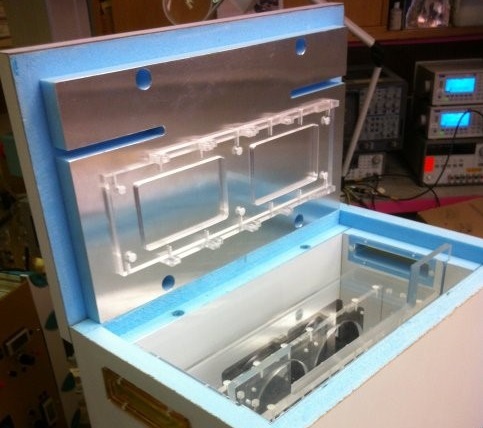
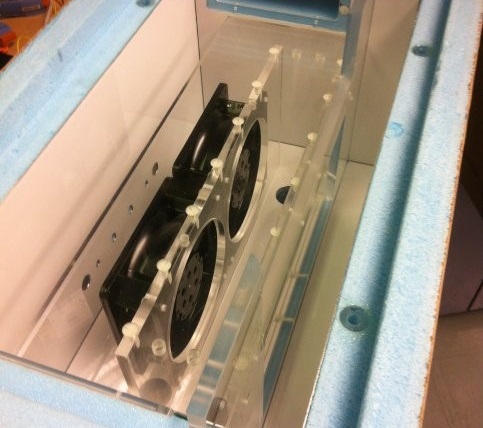
In order to provide realistic operational conditions during the irradiation experiments, some samples have to be kept at low temperatures. Silicon based detectors in the LHC experiments are for example kept cold in order to avoid annealing effects, reduce the leakage current and avoid thermal runaway of sensors and electronics. A typical temperature is from -20°C to -25°C. In the irradiation facilities part of the experiments will thus have to be performed in cold boxes assuring a stable and low temperature during irradiation.
Technical drawing of the cold box
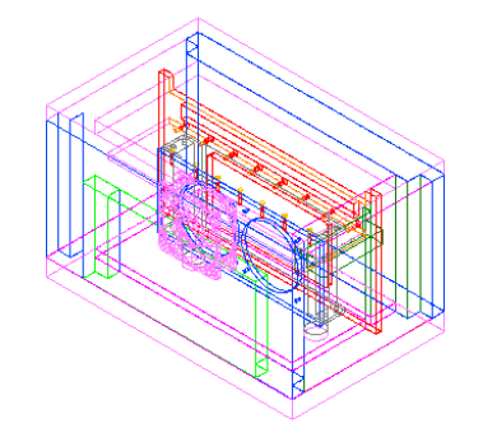
Cold boxes used at CERN



Prepare samples for tables and cold boxes
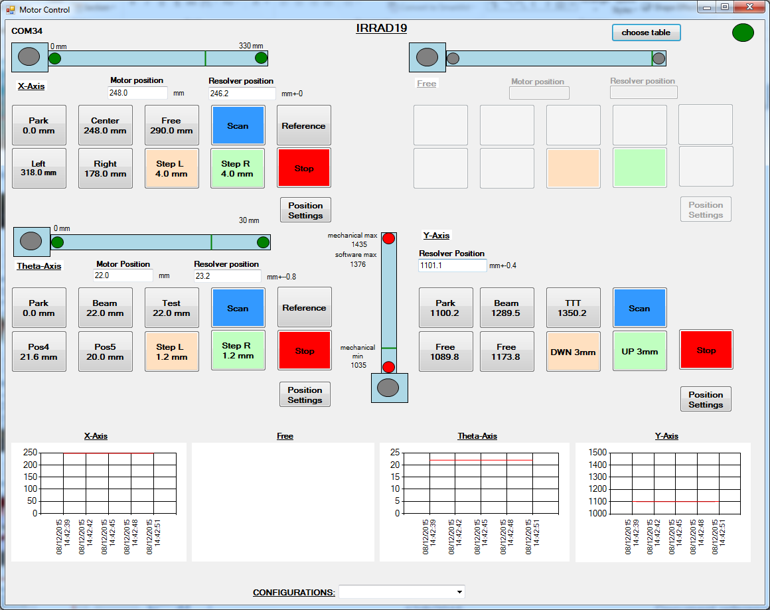
Control system for tables
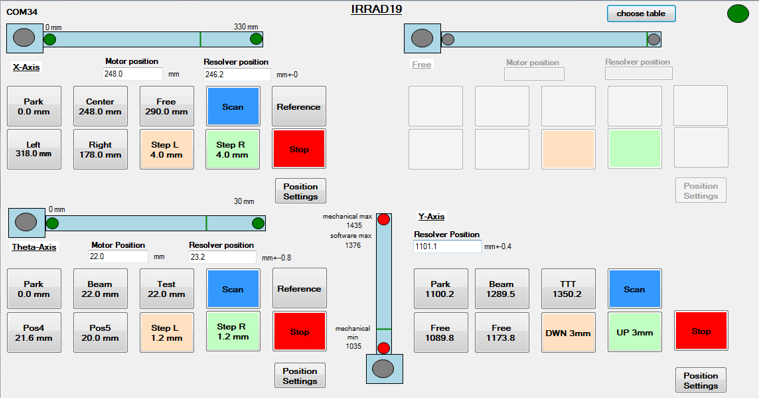
The control system help facility operators control the sample's position during the irradiation experiment. It provides the possibility to configure and communicate with the hardware. The main functionalities include:
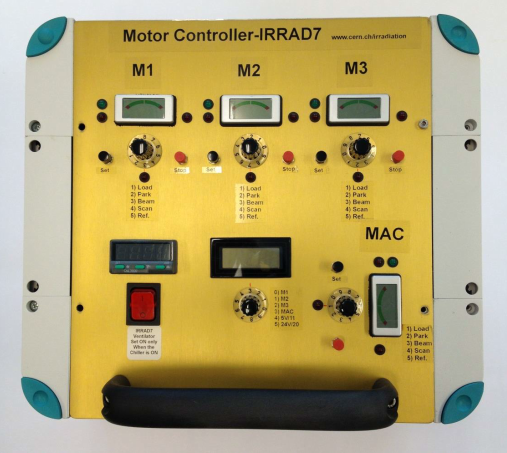

Each table has its own standalone motor driver which is based on a TMC300 3 axis stepper motor controller module from Trinamic. It drives 3 stepping motors, the AC motor and has a temperature controller included for recording and/or controlling temperatures within the sample holder or sample cold box mounted on the table.